Feline diabetes affects up to 1 in 100 cats, leading to excessive thirst, weight loss, and lethargy. Proper management hinges on consistent insulin administration, dietary control, and vigilant monitoring. I’m Dr. Olivia Martinez, a board-certified veterinary internist, here to equip you with a structured care plan to help your diabetic cat enjoy a comfortable, stable life.
1. Recognizing the Signs
Polyuria & Polydipsia: Notable increase in urination and water consumption.
Weight Loss with Increased Appetite: A cardinal sign due to impaired glucose utilization.
Lethargy & Muscle Wasting: Resulting from energy deficits.
2. Diagnostic Confirmation
Blood Glucose Curve: Serial measurements every 2–4 hours post-insulin to tailor dosing.
Fructosamine Test: Reflects average glucose over preceding 2–3 weeks.
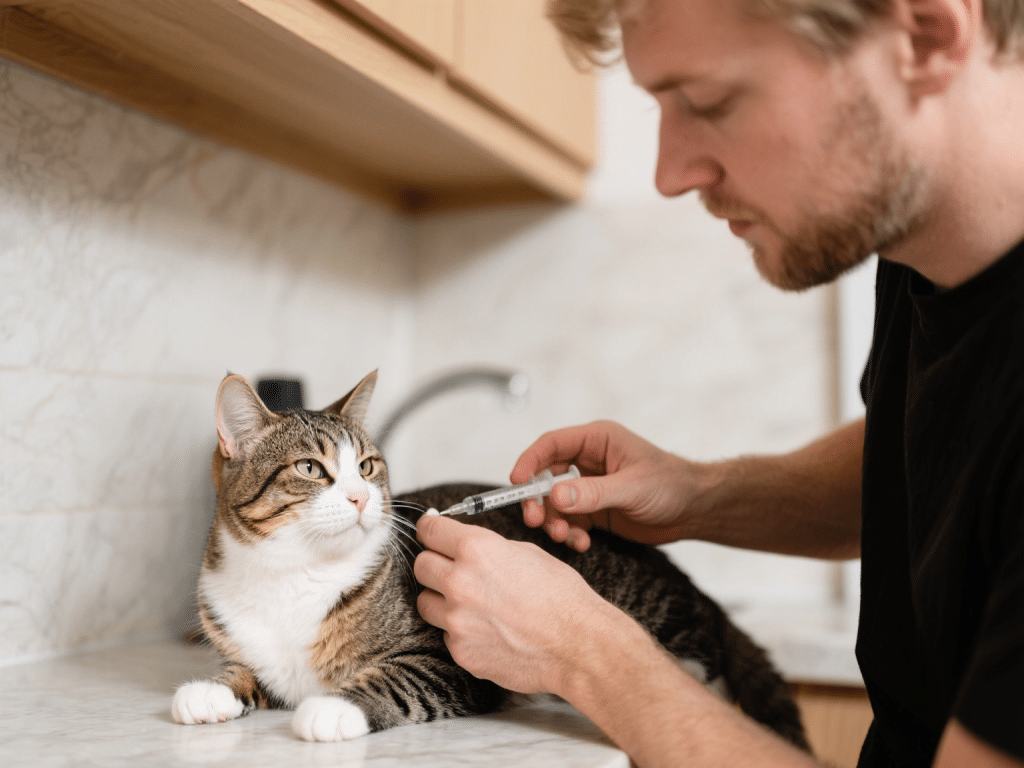
3. Insulin Therapy
Types of Insulin: Lente or glargine often preferred for cats.
Dosing Protocol: Start at 1–2 U per cat twice daily; adjust by 0.5 U increments based on curves.
Injection Technique: Rotate sites—scruff, flank—use fine‐gauge needles for minimal discomfort.
4. Dietary Management
Low-Carbohydrate Diets: Canned foods with <6% carbs on a dry matter basis stabilize glucose peaks.
Consistent Feeding Schedule: Meals timed to insulin peaks (within 15 minutes pre-injection) optimize glycemic control.
5. Home Monitoring
Blood Glucose Checks: Use veterinary glucometer with paw or ear prick; record readings in a logbook.
Clinical Signs Tracking: Monitor appetite, thirst, and weight weekly; report anomalies promptly.
6. Complication Prevention
Hypoglycemia: Emergency feeding of honey or corn syrup if tremors or collapse occur.
Infection Control: Keep injection sites clean to avoid abscess formation.
7. Long-Term Goals
Remission Potential: Up to 50% of cats on low-carb diets can achieve remission in 3–6 months.
Regular Rechecks: Every 3–6 months to assess for remission and adjust insulin needs.
Conclusion
With a disciplined regimen—precise insulin dosing, low-carb nutrition, and diligent monitoring—feline diabetes can be managed effectively. Partner with your veterinary team, stay observant at home, and celebrate each milestone toward remission and stable health.